QVTom
QVTom is a prototypical implementation of the module system for model transformation languages described in [1]. It replaces the default structure of a QVTo transformation with the definition of interfaces and interface implementations where implementations can be linked to interfaces with an export or import relationship.
The changes that have been made to the QVTo plugin [2] are described in this document.
Changes to the AST/CST
Changes to the meta models
Legend:
| Element | Representation |
|---|---|
| CST | CST: ... |
| AST | AST: ... |
| line number in QVTOParser.gi | <n> |
modeltype PCM uses 'http://sdq.ipd.uka.de/PalladioComponentModel/5.0';
modeltype PCM_ALLOC uses 'http://sdq.ipd.uka.de/PalladioComponentModel/Allocation/5.0';
modeltype PCM_REP uses 'http://sdq.ipd.uka.de/PalladioComponentModel/Repository/5.0';
compilation_environment "Commons";
CST: CompilationEnvironmentCS[uriCS = "Commons"]
compilation_environment "EventChannelMiddlewareRegistry";
compilation_environment "EventDistribution";
compilation_environment "EventFilter";
...
interface ISink(
inout pcmAllocation : PCM_ALLOC,
CST: InterfaceInOutParamCS[param = ParameterDeclarationCS[simpleNameCS = "pcmAllocation", typeSpecCS = PCM_ALLOC, directionKind = inout]]
AST: InterfaceRestrictionParameter[param = VarParameter[parsed by original parser]]
inout pcmSystem : PCM_SYS,
inout pcmRepository : PCM_REP,
in middlewareRepository : PCM_REP;
in PCM_ALLOC[Allocation]
CST: InterfaceRestrictionParamCS[param = PCM_ALLOC, classes = {Allocation::TypeSpecCS}, packages = {}] <780>
AST: InterfaceRestrictionParameter
)
AST: InterfaceParamsCS[…]
AST: ModuleHeaderCS[pathNameCS="ISink", interfaceInOutParamsCS=..., interfaceRestrictionParamsCS=...] <581>
{
mapping Sink_createSinkOperationProvidedRole(sinkComponent : pcm::repository::RepositoryComponent,
operationInterface : pcm::repository::OperationInterface) : pcm::repository::OperationProvidedRole;
<830> - declarations: mapping_decl / helper_decl, Klassen: MappingRuleCS, MappingDeclarationCS (with setBlackbox(true));
}
AST: ModuleInterfaceCS[methods = ..., moduleHeader = ..., metamodels = ModelTypes aus Parametern]
CST: ModuleInterface
module Sink mexport ISink
AST: ModuleHeaderCS, ExportCS[pathNameCS = "ISink"] <581>
{
mimport ISEFFRegistry;
mimport ISEFFUtil;
mimport ICommons;
mimport IOperationSignatureRegistry;
mapping Sink_createSinkOperationProvidedRole(sinkComponent : pcm::repository::RepositoryComponent,
operationInterface : pcm::repository::OperationInterface) : pcm::repository::OperationProvidedRole {
entityName := operationInterface.entityName+'OperationProvidedRole'+Commons_getUniqueElementNameSuffix();
providingEntity_ProvidedRole := sinkComponent;
providedInterface__OperationProvidedRole := operationInterface;
}
<851> - implementations of mapping/helper methods: mapping_def / entry_def / helper_simple_def / helper_compund_def, Klassen: MappingMethodCS, MappingQueryCS, ModulePropertyCS
}
Changes to the grammar QVTOParser.gi
%Globals
/.
[...]
import org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.cst.ModuleHeaderCS;
import org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.cst.MappingMethodCS;
import org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.cst.InterfaceInOutParamCS;
import org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.cst.InterfaceParamsCS;
import org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.cst.InterfaceRestrictionParamCS;
./
%End
%KeyWords
[...]
module
interface
mimport
mexport
scope
compilation_environment
%End
%Rules
[...]
unit_element -> compilation_env
compilation_env ::= compilation_environment uri ';'
unit_element -> module_def
unit_element -> interface_def
module_def ::= module_h mexport exportList '{' importList declarationList '}' semicolonOpt
module_h ::= module qualifiedNameCS
exportList ::= qualifiedNameCS
exportList ::= exportList ',' qualifiedNameCS
fullImport ::= mimport qualifiedNameCS ';'
importList ::= %empty
importList ::= importList fullImport
interface_def ::= interface_h '{' interfaceList '}' semicolonOpt
interface_h ::= interface qualifiedNameCS interfaceParams
interfaceParams ::= '(' interfaceInOutParamList ')'
interfaceParams ::= '(' interfaceInOutParamList ';' interfaceRestrictionList ')'
interfaceInOutParamList ::= interfaceInOutParamList ',' interfaceInOutParam
interfaceInOutParamList ::= interfaceInOutParam
interfaceRestrictionList ::= interfaceRestrictionList ',' interfaceRestrictionParam
interfaceRestrictionList ::= interfaceRestrictionParam
interfaceRestrictionParam ::= param_direction typespec '[' typespecList ']'
interfaceRestrictionParam ::= param_direction typespec '[' typespecList ']' '{' typespecList '}'
paramWithDirection ::= param_direction IDENTIFIER ':' typespec
interfaceInOutParam ::= paramWithDirection
typespecList ::= %empty
typespecList ::= typespec
typespecList ::= typespecList ',' typespec
-- returns a MappingRuleCS
interfaceElement -> mapping_decl
-- returns a MappingQueryCS
interfaceElement -> helper_decl
interfaceList ::= interfaceList interfaceElement
interfaceList ::= interfaceElement
-- return a MappingMethodCS
declarationItem -> mapping_def
declarationItem -> entry_def
-- return a MappingQueryCS->MappingMethodCS
declarationItem -> helper_simple_def
declarationItem -> helper_compound_def
declarationItem -> _property
declarationList ::= declarationList declarationItem
declarationList ::= declarationItem
-- changed code ---
scoped_identifier ::= scoped_identifier2
scoped_identifier2 ::= IDENTIFIER '@' IDENTIFIER
%End
The new metamodels
AST
CST
How to include new elements into the CST/AST
- Once: adapt "/org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml.cst.parser/cst/run-lpg.cmd" (LPG_HOME, LPG_EXE, PERL_EXE)
- Warning: spaces in path names can lead to problems
- Augment CST and AST metamodels, generate Java code.
- /org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml.cst.parser/model/QVTOperationalCST.ecore
- /org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml/model/QVTOperational.ecore
- Add new keywords to "/org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml.cst.parser/cst/QVTOKWLexer.gi" (export and rule)
- In "/org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml.cst.parser/cst/QVTOParser.gi"
- Import keywords (%KeyWords)
- Add rules with reference to factory method in org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.cst.parser.AbstractQVTParser
- If possible, call
setOffsetsappropriatelyIn der Regel wenn möglich auch setOffsets entsprechend aufrufen.
- Call "/org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml.cst.parser/cst/run-lpg.cmd"
- If top level elements have been created (such as ModuleImplementation/ModuleInterface/CompilationEnvironment), add them to
org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.cst.parser.AbstractQVTParser.setupTopLevel(EList<CSTNode>)
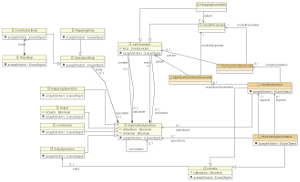
Changes to the CST (/org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml.cst.parser/model/QVTOperationalCST.ecore)
- Changes to UnitCS
- Reference to
ModuleImplementationsandModuleInterfaces
- Reference to
- New: ModuleHeaderCS
- New: ModuleInterfaceCS
- New: InterfaceInOutParamCS
- New: InterfaceRestrictionParamCS
- New: InterfaceParamsCS – eventuell entferenen
- New: ModuleImplementationS
- New: ExportCS
- New: CompilationEnvironmentCS
- Only references the name of a part of the "Compilation Environment", i.e. all files that have to be compiled together.
Changes to the AST (/org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml/model/QVTOperational.ecore)
- New: ModuleInterface
- Interface of a module, defines in/out/inout metamodels, visibility of the metamodel and method signatures
- New: InterfaceInOutParameter
- Same as the in/out/inout parameters of a QVTo transformation but is defined for each ModuleInterface.
- New: InterfaceRestrictionParameter
- Parameter to restrict the visibility of the metamodel
- New: ModuleImplementation
- Implementation of a module, exports at least one interface and has to implement at least the methods of the exported interface(s).
org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.compiler.QVTOCompiler
The entry point for the changes from QVTo to QVTom start in org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.compiler.QVTOCompiler in the method doCompileQVTom, which replaces doCompileQVTo. For the compilation of QVTom in multiple files the following stages are performed:
- Parse all files that are declared as part of the "Compilation Environment" in the file.
- Create
ModuleInterfaces(createModuleInterfaceStubs) for every CST, i.e. start the visitor (QVTOperationalVisitorCS) for every CST (every file). - Resolve all cross references between modules (
crossReferenceModules). Copy all references to every module interface (the elements that are used to resolve calls to methods of foreign modules) between each two environments ofCSTParseResults (of typeQVTOperationalFileEnv). - Compile (CST -> AST) every imported file.
- Perform a transformation of the resulting QVTom-ASTs to a QVTO-AST which can be interpreted/compiled with the default interpreter/compiler.
org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.qvtom2qvto.QVTom2QVToCSTransformation
The linking of method calls etc. is already performed during the compilation. For the transformation from QVTom to QVTo the following steps have to be performed:
- Copy all methods from the module interfaces and module implementations to a new
OperationalTransformation. - Copy in/out/inout parameters to the new transformation.
- Create properties from the modules in the new transformation.
Changes to org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.parser.QvtOperationalVisitorCS
Was modified to be able to handle the new syntax elements.
lookupModelParameter(SimpleNameCS, DirectionKind, QvtOperationalEnv)
Allows the referencing of ModelParameters that are declared in the interface, i.e. the parsed parameters from the ModuleInterface which are InterfaceInOutParameters are made referenceable.
QvtOperationalVisitorCS.genOperationCallExp(...)
If no local mapping can be found, check if a fitting method can be found in an imported module. For this purpose traverse upwards in the environment hierarchy until a fitting environment (of type QvtOperationalFileEnv) has been found and check if one of the imported interfaces implements a fitting method.
visitMappingDeclarationCS(...)
Check the visibility of the context types of the mappings.
visitResolveInExpCS(...)
Allow the resolution of methods in the same ModuleImplementation or in imported interfaces.
New methods for modularity in QvtOperationalVisitorCS
registerModelTypes(...)
Helper method that is used by visitModuleInterfaceand visitModuleImplementation. Parses the used ModelTypes (visitModelTypeCS) and references them in the created Module (getUsedModelType().add(...)), adds them as types to the module (.getEClassifiers().add(...)) and register them in the environment.
visitModuleInterface(...)
Visitor method for ModuleInterfaces, comparable to the visitor methods for methods.
- Register
ModelTypes in the environment. - Register the
ModelInterfacein the environment. - Visit and reference
InOutParametersandRestrictionParameters. - Visit all
MappingDeclarations for methods and reference results.
visitInOutParamsCS(...)
Visitor methods for InOutParameters.
visitRestrictionParamsCS(...)
Visitor method for RestrictionParams. All types are resolved and checked for containment of the package that is to be restricted.
visitModuleImplementation(...)
Visitor method for ModelImplementations.
- Register
ModelTypes in the environment - Create
ModelImplementationand register it in the enviroinment. - Create a new module environment ("moduleEnv") which encapsulates the contained methods and represents the module.
- This is necessary to allow the free distribution of the interfaces and implementations to multiple files.
- Imported interfaces and variables for used meta models are saved in the interface.
- Create properties (
createModuleImplementationProperties) - Resolve exports (
resolveExports), i.e. resolve and reference each interface that is declared as export. - Resolve imports, i.e. resolve and reference each interface that is declared as import.
- Pass through all contained methods
- Register contained method in
moduleEnv(cf.visitMappingModule), i.e. create empty methods that can be referenced. - Visit methods (references to empty methods are resolvable).
- Check if visibility declarations are violated.
validateMethodMetaModelVisibility(ModuleImplementation, QvtOperationalEnv)OCLRestrictedTypeVisitor(ModuleImplementation, QvtOperationalEnv)
- Set entry operation
- Export the methods to the interface, cf.
exportMethodsToInterface(...)`
- Register contained method in
- Pass the errors from the module environment to the parent environment to make them visible in the IDE.
exportMethodsToInterface(...)
In our implementation the method bodies are copied into the interface after the methods are visited (i.e. they are not referenced). We chose this seemingly complicated implementation to allow our modifications to be as non-invasive as possible and to allow the visitor methods for the mappings to perform unchanged.
This method also checks the exported interfaces for complete implementation in the ModuleImplementation and reports errors if necessary.
Meta model visibility validation
The validation of the meta model visibility is realized in two new classes which are explained below. The entry point into the validation can be found in two places:
org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.parser.QvtOperationalVisitorCS.validateMethodMetaModelVisibility(ModuleImplementation, QvtOperationalEnv)QvtOperationalVisitorCS.visitMappingDeclaration(…)
OCLRestrictedTypeVisitor
Is created with a TypeRestrictionSetor a ModuleImplementation. When passing a ModuleImplementation the appropriate .buildFromInterface method of the TypeRestrictionSet is called.
The visitor itself extends OCLAbstractVisitor. Every possible violation of the meta model visibility can be checked and annotated with an appropriate error or warning if necessary.
TypeRestrictionSet
Represents a set of types and packages that are accessible for a particular direction (DirectionKind) and possibly for a particular extent.
QVTo(m)-Environments
Environments are created but not mandatorily persited. They can be used solely for the QVTOperationalVisitorCS and discarded afterwards.
-
org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.parser.QvtOperationalVisitorCS.visitObjectExpCS(ObjectExpCS, QvtOperationalEnv, boolean)-- creates a temporary environment. -
org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.parser.QvtOperationalVisitorCS.visitModuleImplementation(ModuleImplementationCS, QvtOperationalFileEnv)-- create a temporary environent for the module so the parsed methods from different modules in the same file context do not interfere.
org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.env.QvtOperationalEnv
-
org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.env.QvtOperationalEnv.registerMappingOperation(MappingOperation, boolean)- Copy of the equally named method without the boolean parameter. Makes it possible to prevent the registration in the parent environment.
- Additional attributes for the
ModuleImplementations andModuleInterfaces with respective getters and setters. - Additional attribute of type
EntryOperationwhich represents the entry point for the execution of the transformation.
org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.env.QvtOperationalModuleEnv, org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.env.QvtOperationalFileEnv
- Concrete subtypes which allow the getting/setting of
ModuleImplementations andModuleInterfaces.
Import mechanism of QVTo and QVTom
It is already possible to connect multiple transformations by an import mechanism in QVTo. Details for this mechanism can be found in the QVT standard.
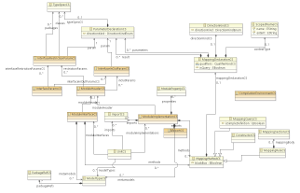
Workflow of the QVTo(m) parser and interpreter

Image after Erweitern eines Code-Editors unter Eclipse um neue Sprachkonzepte by Ivayla Partalina.
Plugins/Packages/Classes
- org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml
- org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.env
- defines the used environments
- type checking
- org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.parser
- QvtOperationalVisitorCS: conversion from CST to AST
- OCLRestrictedTypeVisitor / TypeRestrictionSet / ExtentClassifier / ExtentPackage – meta model visibility validation
- OCLAbstractVisitor – abstract implementation of QVTOperationalVisitor, base for OCLRestrictedTypeVisitor
- QvtOperationalParser – set up the root element for the parse result (UnitCS)
- org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.ast.env
- org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.compiler
- QVTOCompiler – entry point into the compilation
- org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.evaluator
- QvtOperationalEvaluationVisitor / QvtOperationalEvaluationVisitorImpl – interpreter interface and impkementation. adapted to support module implementations and interfaces
- org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.qvtom2qvto
- QVTom2QVToCSTransformation – transformation from QVTom to QVTo (to reuse the QVTo interpreter)
- org.eclipse.m2m.internal.qvt.oml.cst.parser
- AbstractQVTParser – Methods that are called from the parser (LPG).
- org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml.editor.ui
- org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml.runtime
- org.eclipse.m2m.qvt.oml.runtime.ui
Example for parsing and environments
Source code
modeltype ECORE uses 'http://www.eclipse.org/emf/2002/Ecore';
modeltype UML uses 'http://www.eclipse.org/uml2/4.0.0/UML';
interface I_A(
in ecore:ECORE,
out uml:UML
) {
mapping EClass::EClass2Class() : Class;
}
module A mexport I_A {
mapping EClass::EClass2Class() : Class {
name := self.name;
}
}
Partial dump of the resulting CompiledUnit
result = CompiledUnit [
moduleEnvs = [
QvtOperationalFileEnv [
parent = null,
myFile = ".../minimal.qvto",
myModuleImplementations = [
ModuleImplementation[
name = "A",
eOperations = [MappingOperation[name="EClass2Class"]]
]
],
myModuleInterfaces = [
ModuleInterface[
name = "I_A",
operations = [MappingOperation[name="EClass2Class"]]
]
]
]
]
]
See Also
- Modular Model Transformations, the overall approach behind this project, as well as information for developers.
- Xtend2m, a modular extension of Xtend hosted at Github.
References
- A. Rentschler, D. Werle, Q. Noorshams, L. Happe, R. Reussner. Designing Information Hiding Modularity for Model Transformation Languages. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Modularity (AOSD '14), Lugano, Switzerland, April 2014. ACM, New York, NY, USA. April 2014.
- Eclipse Modeling - MMT - Project QVTo
Contributors
- Dominik Werle from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
- Andreas Rentschler from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology